Abstract
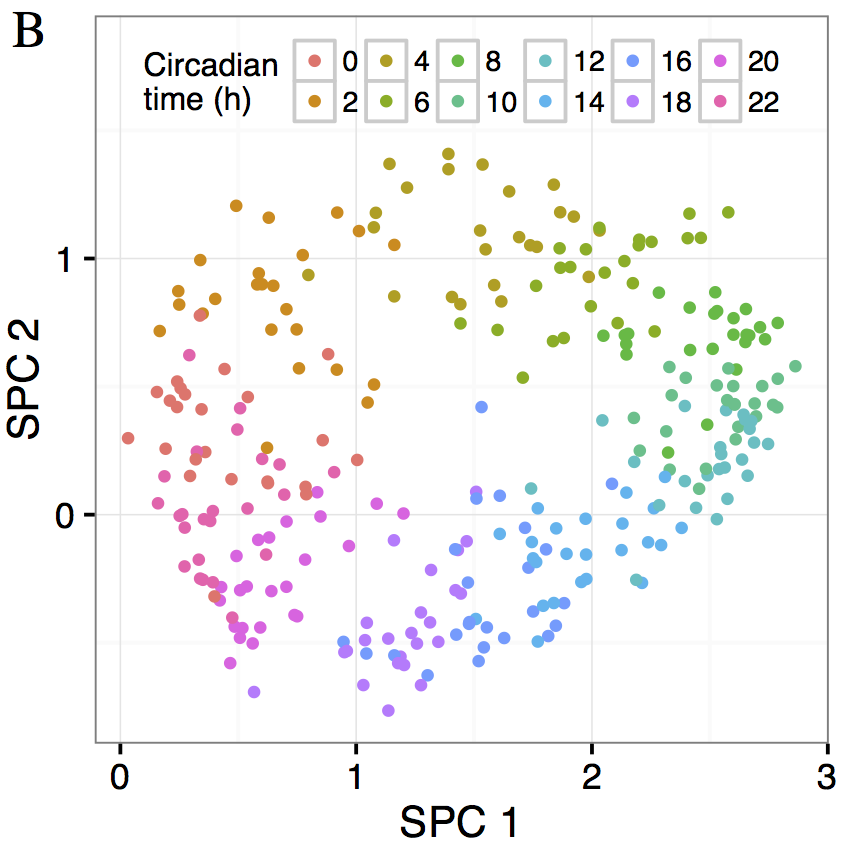
Numerous biological systems oscillate over time or space. Despite these oscillators' importance, data from an oscillatory system is problematic for existing methods of regularized supervised learning. We present ZeitZeiger, a method to predict a periodic variable (e.g. time of day) from a high-dimensional observation. ZeitZeiger learns a sparse representation of the variation associated with the periodic variable in the training observations, then uses maximum-likelihood to make a prediction for a test observation. We applied ZeitZeiger to a comprehensive dataset of genome-wide gene expression from the mammalian circadian oscillator. Using the expression of 13 genes, ZeitZeiger predicted circadian time (internal time of day) in each of 12 mouse organs to within ~1 h, resulting in a multi-organ predictor of circadian time. Compared to the state-of-the-art approach, ZeitZeiger was faster, more accurate and used fewer genes. We then validated the multi-organ predictor on 20 additional datasets comprising nearly 800 samples. Our results suggest that ZeitZeiger not only makes accurate predictions, but also gives insight into the behavior and structure of the oscillator from which the data originated. As our ability to collect high-dimensional data from various biological oscillators increases, ZeitZeiger should enhance efforts to convert these data to knowledge.
Where applicable, full text and supplement provided for fair use.