Abstract
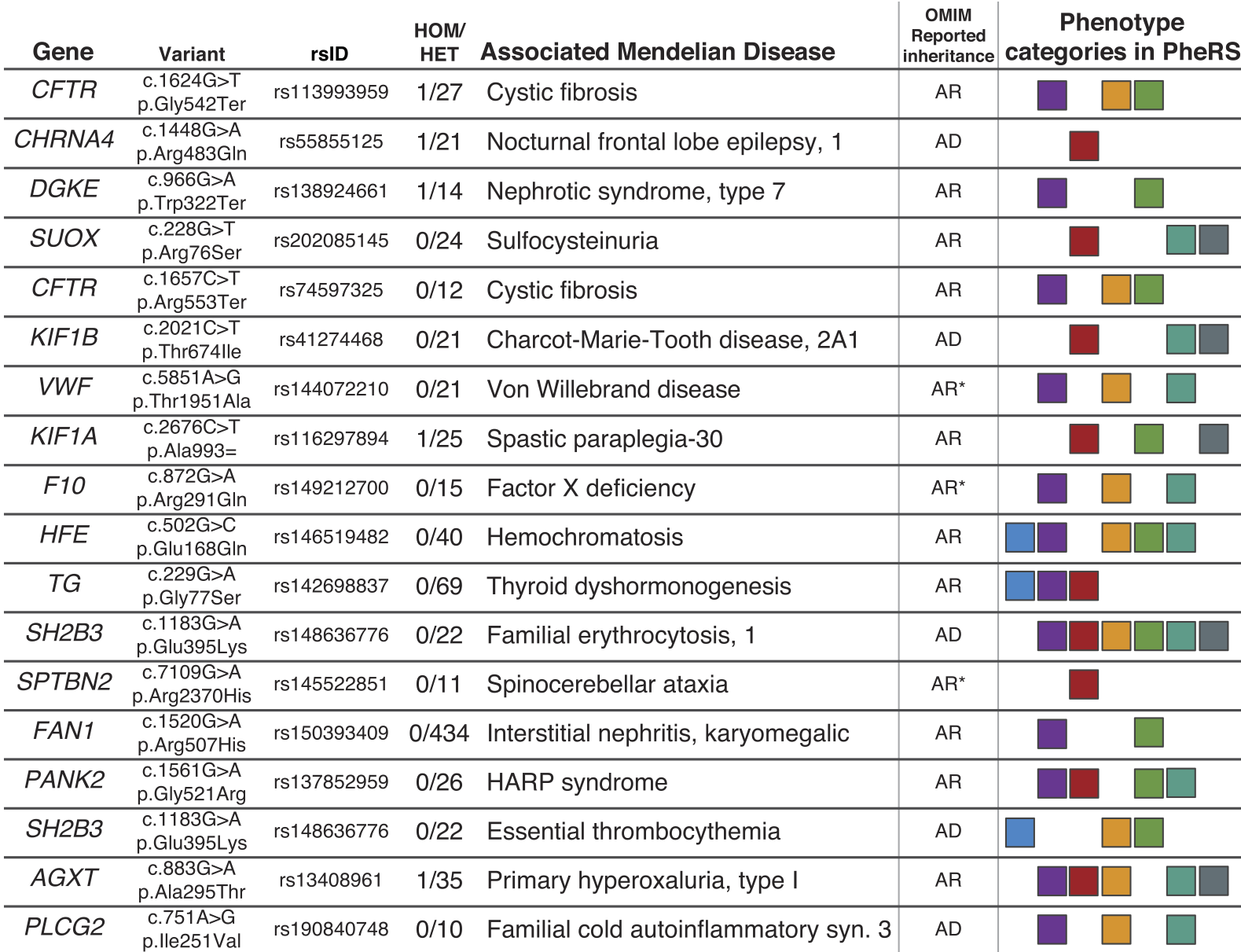
Genetic association studies often examine features independently, potentially missing subpopulations with multiple phenotypes that share a single cause. We describe an approach that aggregates phenotypes on the basis of patterns described by Mendelian diseases. We mapped the clinical features of 1204 Mendelian diseases into phenotypes captured from the electronic health record (EHR) and summarized this evidence as phenotype risk scores (PheRSs). In an initial validation, PheRS distinguished cases and controls of five Mendelian diseases. Applying PheRS to 21,701 genotyped individuals uncovered 18 associations between rare variants and phenotypes consistent with Mendelian diseases. In 16 patients, the rare genetic variants were associated with severe outcomes such as organ transplants. PheRS can augment rare-variant interpretation and may identify subsets of patients with distinct genetic causes for common diseases.
Where applicable, full text and supplement provided for fair use.